Stove Kraft Limited (NSE: STOVEKRAFT) The kitchen appliance manufacturer recorded a contraction in quarterly profitability and sales, pressured by one-time labor provisions and ForEx volatility. Despite the quarterly downturn, the company maintained gross margin expansion and continued its retail footprint expansion toward a 500-store target.
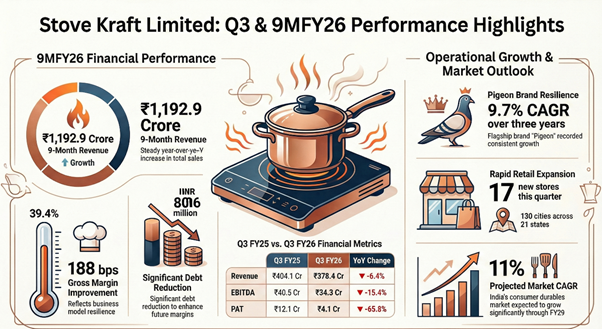
Company reported a decrease in financial performance for the third quarter ended December 31, 2025, with revenue and profit after tax (PAT) declining year-over-year. The results were impacted by a 27% value contraction in the cookware category and extraordinary expenses totaling ₹3.14 crore related to new labor codes and currency fluctuations. However, the company’s nine-month performance remains positive, supported by resilient gross margins and growth in the flagship Pigeon brand.
Operational Drivers
The primary operational driver during the quarter was the continued expansion of the Exclusive Pigeon Stores network. Stove Kraft added 17 stores across 17 cities, taking the total network to 313 outlets spread across 21 states. Management reiterated its target of scaling the exclusive retail footprint to 500 standalone stores by calendar year 2027, with a focus on North and West India.
Alongside network expansion, the company undertook debt reduction measures, lowering debt to ₹806 million. The reduction was aimed at margin improvement and working capital efficiency, supported by sale-and-leaseback transactions.
Financial Performance
For the quarter ended December 31, 2025, revenue from operations stood at ₹378.4 crore, a 6.4% decline from ₹404.1 crore in the prior year. Gross margins improved to 39.4%, up from 37.6% in Q3 FY25, reflecting operational efficiency despite a challenging export environment. The company reported Basic EPS of ₹1.25 for Q3 FY26, down from ₹3.67 in Q3 FY25.
• EBITDA: ₹34.3 crore, down 15.4% year-over-year.
• PAT: ₹4.1 crore, a 65.8% decrease compared to Q3 FY25.
• One-time Expenses: Results were weighed down by ₹1.24 crore for gratuity and leave encashment provisions due to the new labor code and ₹1.90 crore in foreign exchange losses.
Nine-Month (9MFY26) Context:
The broader nine-month performance showed more stability, with revenue up 4.9% at ₹1,192.9 crore and EBITDA growing 4.5% to ₹126.7 crore. However, cumulative PAT for the period saw a slight 3.0% decline to ₹35.9 crore. Basic EPS stands at ₹10.86.
Investment Thesis
Bull Case:
• Margin Resilience: Despite falling revenues, gross margins expanded by 188 basis points, indicating strong pricing power or supply chain efficiency.
• Retail Scaling: The aggressive expansion of exclusive stores (targeting 500 by 2027) provides a direct-to-consumer channel that may shield the company from wholesale volatility.
• Operational Efficiency: Improvement in inventory days (from 144 to 137) and reduction in total debt suggest a strengthening balance sheet.
Bear Case:
• Category Contraction: A sharp 27% drop in cookware value and a 20.4% decline in gas cooktop volume highlight significant demand weakness in core categories.
• Regulatory & Legal Risks: The company is currently contesting income tax demands totaling ₹13.5 crore following search operations in 2023. While management anticipates no material impact, the litigation remains unresolved.
• Earnings Volatility: High sensitivity to foreign exchange fluctuations and one-time labor provisions continues to impact the bottom line.
Business Outlook & Strategy
Stove Kraft’s strategy focuses on a multi-brand approach; Pigeon (value), Gilma (semi-premium), and BLACK+DECKER (premium), to capture different consumer segments. The company intends to leverage its backward-integrated manufacturing facilities in Bengaluru and Baddi to maintain cost leadership. Management is prioritizing the Northern and Western Indian markets for retail expansion, identifying them as regions with significant growth potential. Efficiency gains are also targeted through the working capital cycle, which improved to 43 days in Q3 FY26.
Sector and Macro Context
The Indian consumer durables market is projected to grow at an 11% CAGR through FY29, though the current quarter witnessed muted demand across the segment. Macroeconomic indicators show retail inflation at 1.33% for December 2025 and falling unemployment (4.8%), which is expected to bolster future household consumption. However, the sector faces headwinds from subdued export momentum due to ongoing trade negotiations and tariff structures between India and the United States.

