In a move to cement India’s position as a global technology powerhouse, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman unveiled the Union Budget 2026-2027, placing “cutting-edge technologies” and “frontier sectors” at the heart of the nation’s economic strategy. The budget outlines a robust roadmap for emerging technologies, signaling a shift from traditional manufacturing to high-tech, IP-driven industrial growth.
Major Sectoral Allocations & Highlights
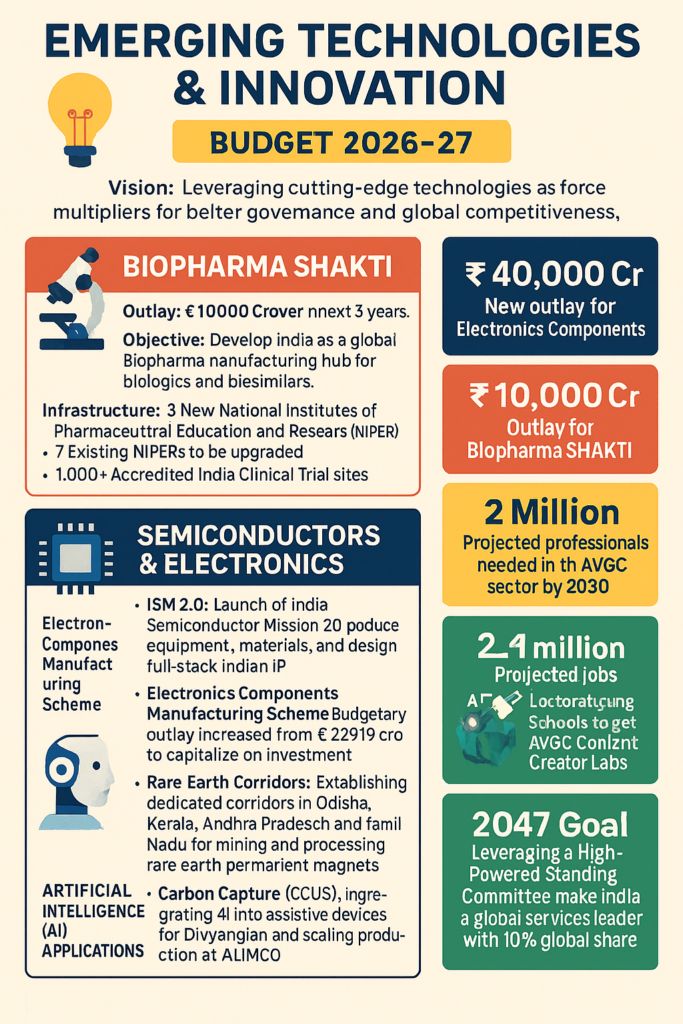
The government has significantly scaled up its financial commitment to the technology ecosystem through several flagship missions:
- India Semiconductor Mission (ISM) 2.0: Building on the success of the first phase, the government launched ISM 2.0. This phase shifts focus toward producing specialized equipment and materials, designing full-stack Indian Intellectual Property (IP), and fortifying domestic supply chains.
- Electronics Manufacturing: The outlay for the Electronics Components Manufacturing Scheme has been nearly doubled, increasing from ₹22,919 crore to ₹40,000 crore to capitalize on current investment momentum.
- Biopharma SHAKTI: A new initiative, “Strategy for Healthcare Advancement through Knowledge, Technology and Innovation” (SHAKTI), was introduced with an outlay of ₹10,000 crore over five years to transform India into a global hub for biologics and biosimilars.
Emerging Industry Trends
- The budget highlights a clear trend toward the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) as a “force multiplier” for governance and industry. Key developments include:
- AI in Agriculture: Under the “Bharat VISTAAR” program, the government is integrating AgriStack portals with AI systems to provide data-driven insights to farmers.
- Hi-Tech Infrastructure: The establishment of Hi-Tech Tool Rooms by CPSEs—digitally enabled, automated service bureaus—aims to locally design and manufacture high-precision components at scale.
- Digital Content Creation: In a nod to the growing “Orange Economy,” the budget proposes setting up AVGC (Animation, Visual Effects, Gaming, and Comics) Content Creator Labs in 15,000 secondary schools and 500 colleges.
Market Perspective & Tax Reforms
To attract global tech giants and foster a data-driven economy, the budget introduced significant tax concessions:
- Cloud & Data Centers: Foreign companies providing cloud services through India-based data centers will receive tax holidays until 2047. Additionally, data center services provided from India will benefit from a 15% Safe-Harbor margin on costs.
- IT Services Simplification: The Safe-Harbor threshold for IT services has been aggressively raised from ₹300 crore to ₹2,000 crore, with an automated, rule-driven approval process to reduce litigation.
Industry analysts view these measures as a decisive step toward “Viksit Bharat” (Developed India). By prioritizing “action over ambivalence” and “reform over rhetoric,” the government aims to maintain a steady GDP growth rate of around 7% while reducing critical import dependencies in the tech sector. The focus on domestic IP and high-value manufacturing marks a transition for the Indian market from being a global back-office to a leading laboratory for global innovation.

